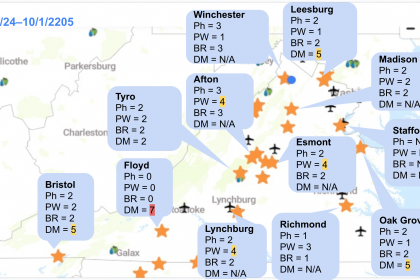
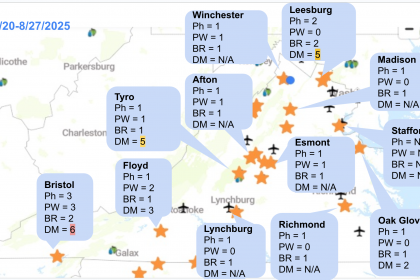
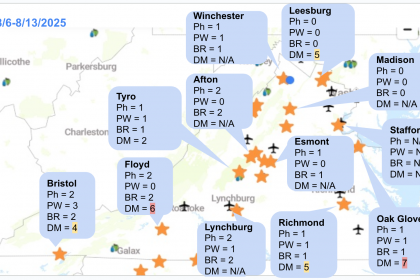
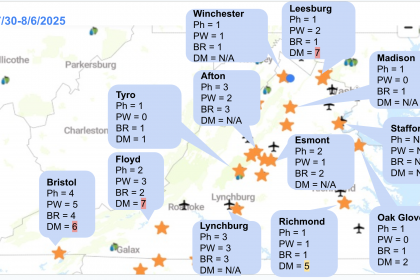
Here are snapshots from the last week, showing the number of days with the risk of each disease: Ph = Phomopsis, PW = Powdery mildew, BR = Black rot, and DM = Downy mildew. N/A means there is no data or some issues with the NEWA (which has been reported). The letter in parentheses indicates L = Low risk, M = Moderate risk, and H = High risk of downy mildew based on our model, which includes the next 48 hours forecasted weather.
It looks like the west of the Blue Ridge Mountains had more rain than the east. Since we are still in the critical period for cluster infections, please keep an eye on the weather forecast and act accordingly.
For the detailed recommendations, please check our pest management guides, the previous post about at bloom protection, and the slides from our last meeting.
The following is more or less a condensed version of the critical period grape disease management tips.
Disease-Specific Fungicide Recommendations at bloom time (= critical stage when clusters are susceptible to infections, at bloom to 6-8 weeks for V. vinifera, 4-5 weeks for V. labrusca, and 5-7 weeks for hybrids)
Protective applications are more effective than after-the-fact sprays.
Downy Mildew:
- Protective Materials: Mancozeb (FRAC M3), Captan (FRAC M4), fixed copper (FRAC M1), Revus or Forum (FRAC 40), Zampro (FRAC 40 + 45), and Ranman (FRAC 21).
- Kick-back Materials: Ridomil (FRAC 4), Phosphonates (FRAC P07)
- Resistance Note: Be aware of increasing cases of Revus-resistant downy mildew isolates, particularly in Virginia. Some questions on phosphonate materials (FRAC P07).
Powdery Mildew:
- Cost-Effective Options: Sulfur (FRAC M2) and copper (FRAC M1).
- Other Materials: DMI fungicides (FRAC 3), Quintec (FRAC 13), Vivando (FRAC 50), Luna Experience (FRAC 7 + 3), Topguard EQ (FRAC 11 + 3), Aprovia (FRAC 7), Aprovia Top (FRAC 7 + 3), Miravis Prime (FRAC 7 + 12), and Torino (FRAC U6).
- Resistance Note: There is widespread resistance to QoI (FRAC 11) and DMI (FRAC 3) in Virginia. Plus a case of Quintec resistance.
Black Rot:
- Protective Materials: Mancozeb, QoI fungicides (FRAC 11), and DMI fungicides (FRAC 3).
- Kick-back Materials: DMI fungicides and QoI (weaker than the DMI).
- Ineffective Options: Captan and copper are not effective against black rot.
- Resistance Note: Some questions about FRAC 3 (DMI fungicides)
Botrytis (Gray Mold):
- Recommended Materials: Rovral and Meteor (FRAC 2), Elevate (FRAC 17), Vanguard and Scala (FRAC 9), Luna Experience (FRAC 7 + 3), Kenja (FRAC 7), Miravis Prime (FRAC 7 + 12), and Switch (FRAC 9 + 12).
- Resistance Note: QoI fungicides are no longer the most effective choice due to the emergence of QoI-resistant Botrytis strains. Many materials are considered moderate to high risk.
Ripe Rot:
- Recommended Fungicides: Mancozeb, ziram (FRAC M3), captan (FRAC M4), Aprovia (FRAC 7), Switch (FRAC 9 + 12), Rovral (FRAC 2), and QoI (Strobilurin, FRAC 11).
- Resistance Note: Surveys have found numerous cases of QoI-resistant isolates for ripe rot.
Fungicide Resistance Management Strategies
To effectively manage fungicide resistance and ensure the long-term efficacy of your disease control program, consider the following recommendations:
- Rotate Modes of Action: Always rotate fungicides by using different FRAC (Fungicide Resistance Action Committee) groups. This prevents pathogens from developing resistance to a single type of chemical.
- Limit Use of Specific FRAC Codes: As a general rule, limit the use of any particular FRAC code to no more than twice per growing season, with the exception of those beginning with the letter “M” (which are typically multi-site contact fungicides with a lower risk of resistance development).
- Tank Mixing
- For downy mildew, you can mix one of the recommended materials with mancozeb, captan, or copper.
- For black rot, you can mix with manczeb.
- For powdery mildew, always mix a powdery mildew material with either sulfur or copper.
- For Botrytis, combine one of the recommended materials with either captan or copper in your tank mix.
- For ripe rot, in addition to rotating modes of action, use a tank mix that includes at least two different modes of action.
These strategies are crucial for sustainable disease management and for combating the increasing prevalence of fungicide resistance in vineyards.